A colloquio con Dott. Andrea Garelli specialista in Chirurgia Plastica Ricostruttiva ed Estetica
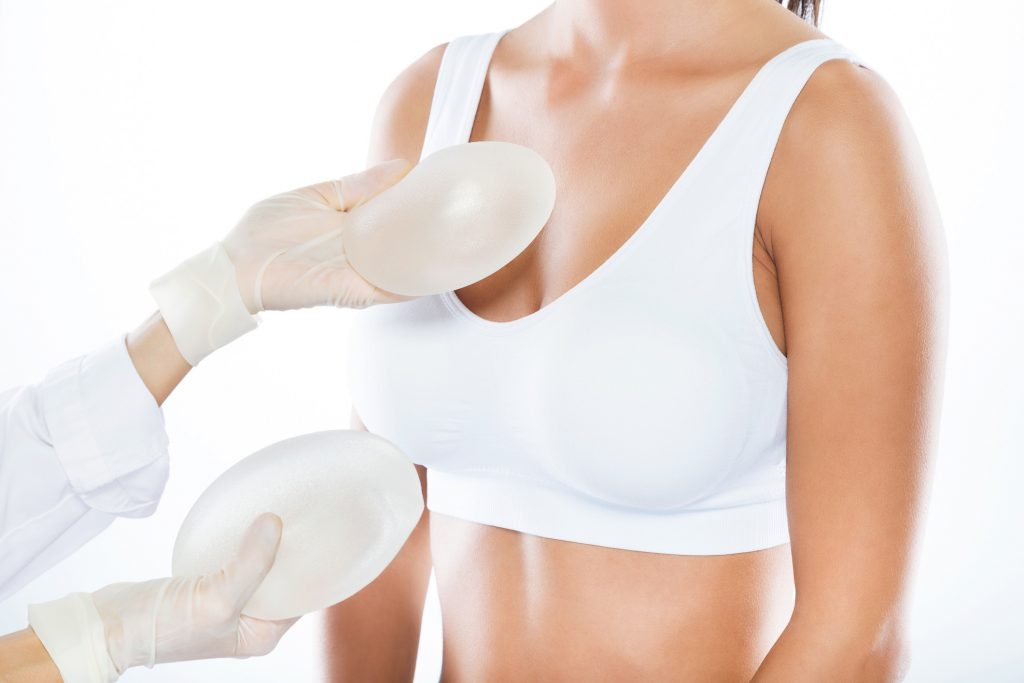
Sono un chirurgo plastico e mi occupo diestetica quindi di protesi al seno ne inserisco mole ogni anno ed ormai da qualche anno, quindi vi lascio immaginare le centinaia di telefonate, sms, mail che ho ricevuto da pazienti spaventate per questa assurda storia.
Assurde se analizziamo le dichiarazioni del propetario della società PIP ed i numeri di questa (400/500.000 coppie di protesi in tutto il mondo).
Le protesi PIP hanno due problemi fondamentali; il silicone scadente all’internoe l’involucro troppo sottile. Questo comporta una facilità maggiore di rottura e la possibilità che questo silicone non omologato possa indurre tumori e non solo al seno ma ovunque arrivi.
Questo non significa rottura o tumore certo!
Le signore che hanno queste protesi non hanno un rischio maggiore di tumore se le protesi sono integre, il problema può subentrare solo dopo la rottura delle protesi ed il prolungato contratto tra il silicone ed il tessuto mammario.
Cosa fare?
-Controllare il certificato di garanzia che viene consegnato dal chirurgo plastico alla paziente dopo l’intervento
-Se siete portatrici di protesi PIP dovete subito eseguire un ecografia mammaria per vedere lo stato delle protesi e poi tornare dal chirurgo per concordare con lui la condotta da tenere (controlli a breve tempo/sostituzione delle protesi).
-Se il certificato ed il chirurgo vi hanno rassicurato sul tipo/marca di protesi che vi hanno impiantato non dovete fare nulla di nuovo.
Termino dicendo ‘chi è causa del propio mal pianga se stesso’ perchè non credo alla versone delle pazienti che adesso hanno scoperto delle protesi di marca PIP, inquanto se si sono rivolte ad un medico non specializzato in chirurgia plastica, che non lavorava in cliniche o day surgery in regola ed applicava dei prezzi troppo bassi doveva capire che forse c’era qualcosa che non andava.
Per quelle che invece si sono rivolte allo specialista e comunque si trovano delle protesi scadenti senza esserne state informate prima il problema non sono le protesi ma la truffa che il medico le ha fatto.
A tutte le mie pazienti dico con molta serenità e sicurezza… godetevi il risultato senza preoccuparvi di nulla…